lateral flexion compression test|cubital tunnel syndrome elbow flexion : ODM The Kemp test (also known as the quadrant test and extension-rotation test) is a provocative test useful for diagnosing pain related to facet joint pathology, e.g. osteoarthritis. The client performs combined extension and rotation of the spine (used for the cervical spine or the lumbar spine). 19 de jul. de 2021 · Ao todo há sete patentes globais no game, que vão do Bronze ao Desafiante, e constam com 18 subdivisões. Para atingi-las, é preciso conquistar determinados valores de pontos de acordo com a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Orbit 360° Dining. Level 52, Sky Tower Corner of Federal and Victoria Streets Auckland. Phone: (09) 363 6000, book online, or email [email protected] Opening Hours. Lunch Friday to .
The Kemp test (also known as the quadrant test and extension-rotation test) is a provocative test useful for diagnosing pain related to facet joint pathology, e.g. osteoarthritis. The client performs combined extension and rotation of the spine (used for the cervical spine or the lumbar spine). The Spurling test, as it was originally described, was performed by passive lateral flexion and compression of the head, though this is no longer considered the proper . Active Compression test ("O'Brien's Test") positive for SLAP tear when there is pain is "deep" in the glenohumeral joint while the forearm is pronated but not when the forearm .With patient standing, sitting, or lying supine, use both hands to compress the lateral sides of the rib cage inward towards the sternum. With the patient lying on their side, use both hands on .
The cervical spine is passively and maximally rotated away from the side being tested. While maintaining this position, the spine is gently flexed as far as possible moving the ear toward .
In the classic Spurling test, the neck is passively hyperextended and laterally flexed toward the symptomatic side. The test is positive for cervical radiculopathy if axial loading to .Cervical flexion-extension, lateral flexion and rotation will be assessed with bedside instruments. This would aid in increasing accuracy and precision of objective measurement while .
presence of mdl impacts factors test
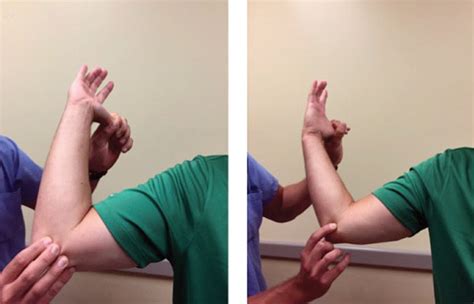
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome is a compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerve at the elbow, and is the 2nd most common compression neuropathy of the upper extremity. It typically presents with paresthesias of the small and .
The Spurling test, as it was originally described, was performed by passive lateral flexion and compression of the head, though this is no longer considered the proper technique. The test is most commonly defined in the current literature as the passive cervical extension with rotation to the affected side and axial compression. Lateral patellar compression in flexion must be confirmed by clinical examination. Focal tenderness is present at the inferomedial patella and/or the anteromedial joint line. . There is no effusion or crepitus, and the . Originally titled the ‘Neck Compression test,’ the test has been referred to as the ‘Spurling Compression test’, ‘Spurling’s . has evolved to include multiple methods. Anekstein et al. determined the method of extension, lateral flexion, and axial compression to cause the ‘highest VAS score and most distally elicited pain .
Introduction [edit | edit source]. Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the physical assessment and providing a tentative diagnosis. Special testing is generally performed following a full .
The Femoral Nerve comes from the Lumbar plexus, see link.The femoral nerve lies within the femoral triangle which is bounded by the inguinal ligament (superiorly), the medial border of the Sartorius muscle and the lateral border of the Adductor Longus muscle (The muscles Pectineus and Iliacus and Psoas lie within this triangle as well). The femoral nerve lies (most laterally) . Lateral Patellar Compression Syndrome . Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive McMurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies. . prone-flexion compression. Thessaly test. standing at 20 degrees of knee flexion on the affected limb, the patient twists with knee external and internal rotation .C3- Neck lateral flexion; C4- Shoulder elevation; C5- Shoulder abduction; C6- Elbow flexion/wrist extension; C7- Elbow extension/wrist flexion; . found Arm Squeeze test useful to distinguish between cervical nerve root compression and shoulder disease. The test has 96% for both sensitivity and specificity, inter-observer value of 0.81 and . Positive test (i.e., lateral aspect of patella is fixed and cannot be raised to at least horizontal position) indicates tight lateral structures . 45 degrees of knee flexion. Abnormalities of .
lateral flexion. rotation. Shoulder range of motion. Compare active and passive motion, both sides . (somewhere between flexion and abduction) pain is elicited (positive test) as the greater tuberosity impinges against the acromion (between 70-110°) . (Active Compression test)The Noble’s test (Noble's Compression test) is a provocative test of the iliotibial band, developed by Clive Noble. . When approaching the knee joint, the iliotibial tract passes the lateral epicondyle of the femur and splits into two structures: the iliopatellar band, . (often at 30° of flexion) indicates ITB syndrome. Evidence [edit .
Lumbar Orthopaedic Tests Palpation Spinous Processes Descriptive Anatomy The five lumbar spinous processes are large and easily palpable with the spinal column in the flexed position (Fig. 10-1). The fifth lumbar vertebra is the lowest movable segment. In 5% of the population, the fifth lumbar vertebra is congenitally fused to the sacrum, a condition called.Performing the Test: With patient standing, sitting, or lying supine, use both hands to compress the lateral sides of the rib cage inward towards the sternum. With the patient lying on their side, use both hands on the lateral side of the rib cage that is facing upward to compress the ribcage towards the table. Positive Test Examination may reveal pes planus or another deformity, malalignment, or muscle atrophy in severe cases. 18 The pain can be reproduced by tapping along the course of the nerve (Tinel sign) and .Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a labral tear or acromioclavicular lesion. Test Position: Sitting or standing Performing the Test: The patient is instructed to place the shoulder into 90 degrees of flexion and 10 degrees of adduction. Next, the arm is actively internally rotated so the thumb is pointing downward. The instructor then applies a inferior directed force (into .
The standing flexion test is a test that can be used to assess sacroiliac joint dysfunction. It is best used in combination with other specific tests. . Rücklauf, Faber test, scral thrust, compression test . is preferable. “Cibulka et al. (1988) investigated the reliability of a combination of four . more commonly seen with Guyon's canal compression due to unopposed FDP flexion. distal biceps tendon rupture. medial ecchymosis and swelling. . lateral pivot-shift test . patient lies supine with affected arm . Jackson compression test: Dural sheath, nerve root, spinal nerve: Radicular pain: Spurling compression test: Dural sheath, nerve root, spinal nerve: . FIG. 3-6 Lateral flexion assessed with an inclinometer. A, With the patient seated and the cervical spine in a neutral position, the examiner places one inclinometer on the T1 spinous process .
pressure film impact testing
The FABER (Patrick’s) Test stands for: Flexion, Abduction and External Rotation. These three movements combined result in a clinical pain provocation test to assist in diagnosis of pathologies at the hip, lumbar and sacroiliac region. . The leg is placed in a figure-4 position (hip flexed and abducted with the lateral ankle resting on the .
Noble compression test: This test starts in supine posture and a knee flexion of 90 degrees. As the patient extends the knee the assessor applies pressure to the lateral femoral epicondyle. If this induces pain over the lateral femoral epicondyle near 30-40 degrees of flexion, the test is considered positive.
Importance of Test: The gapping pressure gaps takes pressures off (or gaps) the anterior side of the SI joint and compresses the posterior side of the joint. The compression force takes pressure off (or gaps) the posterior side of the SI joint and compresses the anterior side of the joint.The diagnostic validity of the cervical flexion-rotation test in C1/2 related cervicogenic headache. Man Ther 2007;12:256-262; ↑ 4.0 4.1 Smith et al. The influence of age, gender, lifestyle factors and sub-clinical neck pain on the cervical flexion-rotation test and cervical range of motion. Manual Therapy 2008;13:552-559 Cervical radiculopathy is a clinical condition characterized by unilateral arm pain, numbness and tingling in a dermatomal distribution in the hand, and weakness in specific muscle groups associated with a single cervical nerve root. It is caused by nerve root compression in the cervical spine either from degenerative changes or from an acute soft disc hernation.
pressure vessel impact testing
In 1990, they came up with the cervical rotation lateral flexion test to assess hypomobility of the first rib, and in 1992 assessed the test’s inter-rater reliability and validity against cineradiography in assessing first rib elevation. In a sample of 23 patients, they found an excellent Kappa value of 1 and a positive test correlated with .neck pain with radiating pain/cervical radiculopathy, including the upper limb tension test, Spurling's test, distraction test, and the Valsalva test. Cranial cervical flexion and neck flexor muscle endurance tests may be use in assessing movement coordination impairments, and algometric assessment of pressure pain threshold may be useful in .Cubital tunnel syndrome (CBTS) is a peripheral nerve compression syndrome. It is an irritation or injury of the ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel at the elbow. This is also termed ulnar nerve entrapment and is the second most common compression neuropathy in the upper extremity after carpal tunnel syndrome. It represents a source of considerable discomfort and disability .
The test 4 is performed by placing the arm in forced flexion with the arm fully pronated . The scapula should be stabilized during the maneuver to prevent scapulothoracic motion.
flexing shoulder and elbow test
webLes Jeux Flonga sont des petits défis sympas de Flonga.com. Tu trouveras ici des jeux d'action passionnants, des jeux de réflexion astucieux, des jeux de course rapides, des jeux point'n'click amusants, des matchs IO passionnants et bien plus encore. Si tu n'arrives pas à te décider sur un genre de jeu, mais que tu veux l'énorme sélection de jeux amusants, .
lateral flexion compression test|cubital tunnel syndrome elbow flexion